
Managing conflict in the company: 5 proven methods

Conflicts in the workplace lead to absenteeism and reduced commitment. Effective conflict management helps to minimize the negative consequences of tensions and prevent them from escalating. In this article, we present 5 proven methods for resolving conflicts constructively and bringing about lasting positive changes in the working atmosphere.
What is conflict management?
Conflict management encompasses all measures for identifying, investigating and resolving conflicts in the workplace. The aim is to reduce tensions at an early stage and develop constructive solutions.
Conflict management includes in particular:
- Conflict analysis
- Moderation and mediation between conflicting parties
- Constructive discussion
- Development of sustainable solutions
- Conflict prevention measures
Typical conflicts in companies
Conflicts often arise in companies in the following constellations:
- Between colleagues at the same level
- Between employees and managers
- Between departments
Typical causes of such conflicts are communication problems, unclear responsibilities, different expectations and values as well as competitive situations and pressure to perform.
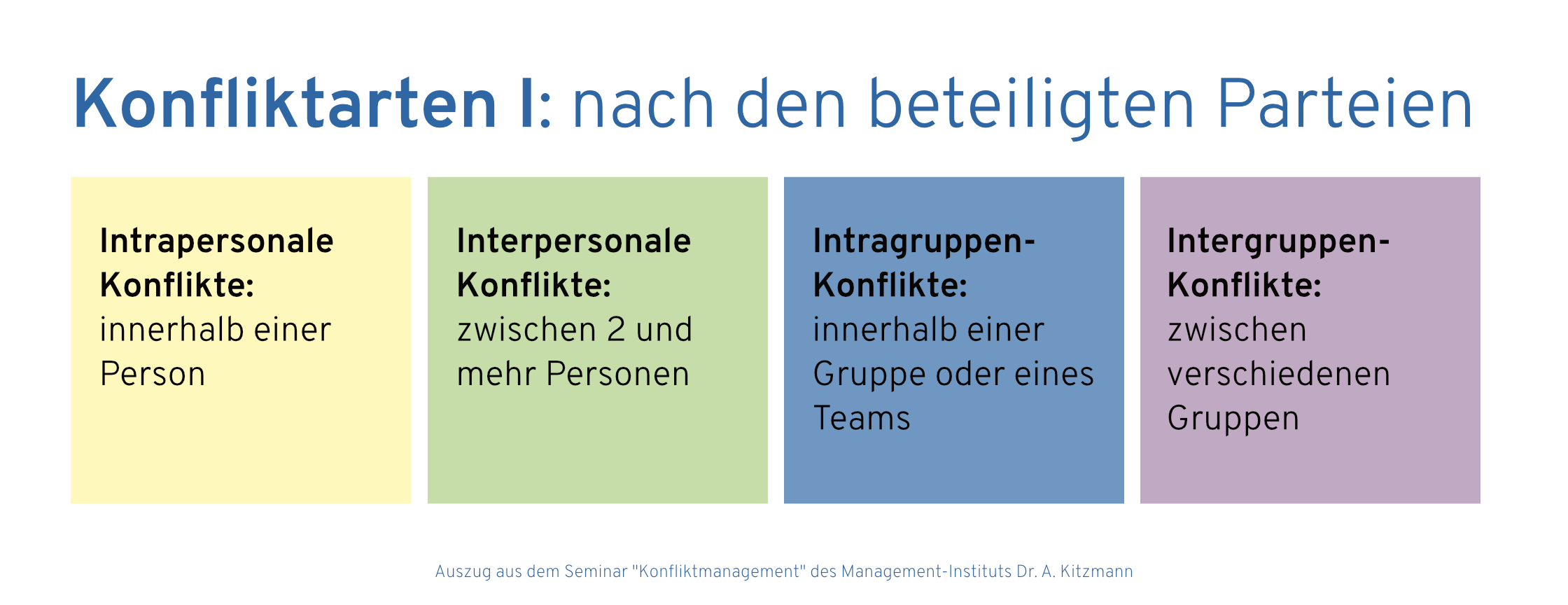
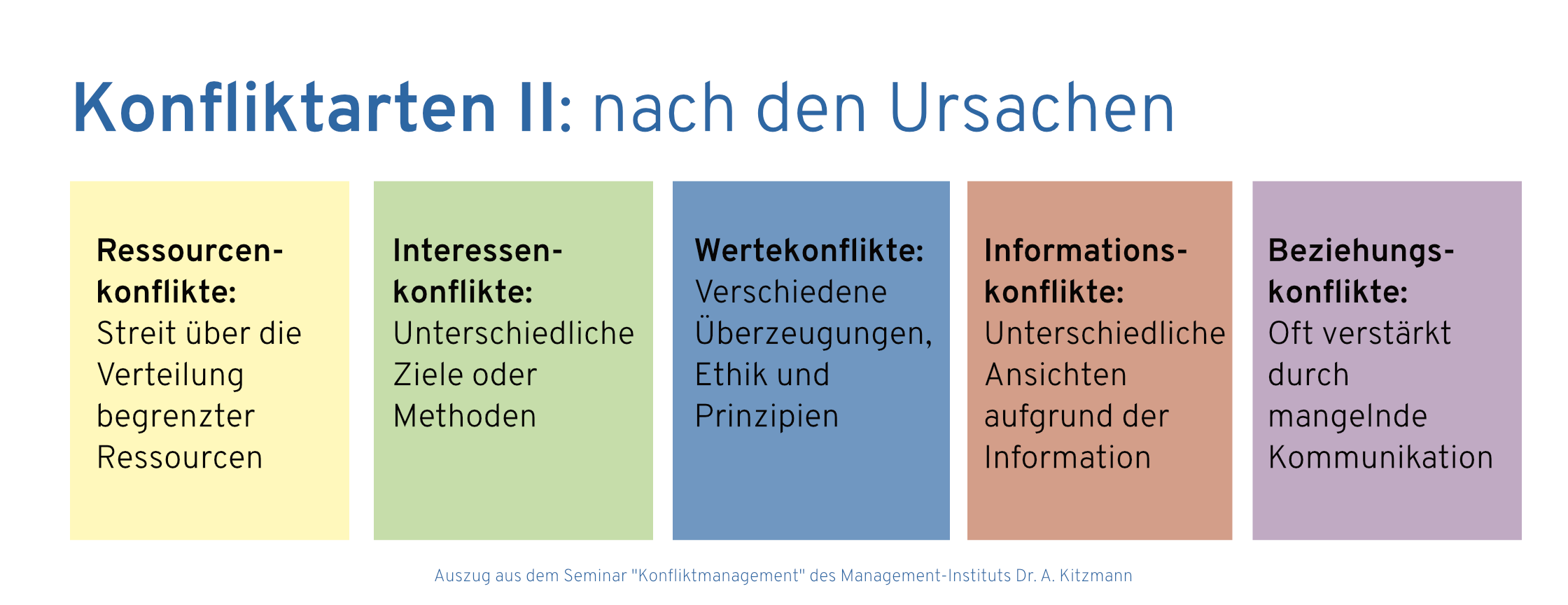
Negative effects of smouldering conflicts
A poor working atmosphere and unresolved conflicts reduce employee motivation and lead to a loss of productivity for companies. This is because unresolved conflicts increase the absenteeism of the employees concerned, which in turn is associated with costs for the company. Each day of absence costs a company an average of 330.40 euros[1]. Employees with a low emotional attachment, which can be caused by conflicts, are absent for an average of 7.7 days, while employees with a high emotional attachment are only absent for 5 days. A company with 2,000 employees could therefore save more than 1.6 million euros a year if emotional attachment were improved through conflict management.
Proven conflict management methods
Method 1: Mediation
In mediation, a neutral third party intervenes in the conflict. The mediator's task is to reach an agreement and work out a joint solution with the conflicting parties. This is suitable when fronts are hardened and both parties show interest in a joint solution. However, if both parties refuse to cooperate, this method is difficult to use.
Example: Two departments are arguing about the allocation of resources. An external and impartial mediator guides both sides through a discussion and works out a solution with which both sides are satisfied.
Method 2: Moderation
Moderation, on the other hand, is a less intrusive process. A neutral person ensures that the discussion between the conflicting parties remains constructive. The moderator tends to remain in the background without developing direct solutions. Moderation can be used when conflicts are addressed openly and the exchange needs to be moderated in a structured manner. In contrast to mediation, moderation is not suitable for highly emotionalized conflicts
Example: Two employees have regular conflicts in meetings about project responsibilities. A moderator accompanies a discussion and ensures that the conversation between the conflicting parties remains fair.
Method 3: Conflict coaching
In conflict coaching, managers or teams learn to better recognize conflicts, reflect on their behaviour and find constructive strategies for conflict resolution. This is suitable for teams that regularly get into conflicts and want to manage them better. If acute solutions are required and there is no room for long-term reflection, this method is not suitable.
Example: A team regularly gets into conflict due to different working styles and communication. Through conflict coaching, the team members learn to build mutual understanding and reach clear agreements on how to work together. After coaching, there are fewer misunderstandings and the team works together more harmoniously.
Method 4: Escalation talks
Escalation talks follow clear rules in order to de-escalate highly emotionalized conflicts and record binding solutions. While mediation and moderation work towards an amicable solution and take place in a more cooperative and protracted process, escalation talks aim to find a quick and binding solution when the conflict has already escalated to a high level. They should therefore be used in escalated conflicts if the working atmosphere is impaired. For minor conflicts, other methods such as mediation or moderation should be used, as these create a more open and less confrontational framework
Example: A conflict between two employees threatens to affect the entire team. The manager conducts a structured escalation meeting to quickly de-escalate the conflict and find a binding solution that stabilizes the working environment again.
Method 5: Team development
Team development is a preventative measure to strengthen cooperation and trust within the team. It helps to prevent conflicts or recurring tensions within the team. However, it is not suitable as the sole measure for acutely escalated conflicts.
Example: Regular tensions arise due to a lack of trust in the team. Team-building activities strengthen cohesion.
The right expectations in conflict resolution
When resolving conflicts, expectations should be realistic. Not every conflict can be completely resolved, but improvements can usually be achieved. Possible results are the restoration of good cooperation or at least mutual respect. However, some conflicts remain permanent, especially if fundamental values are affected. In such cases, it is important to agree on rules for respectful cooperation.
The role of the manager in conflict management
Managers play an important role in conflict management. They need communication skills, empathy, neutrality and assertiveness to resolve conflicts successfully. These skills can be specifically improved through seminars and coaching. Managers should receive regular training in order to recognize conflicts at an early stage and respond to them professionally.
Die Rolle der Führungskraft im Konfliktmangement
Führungskräfte spielen eine wichtige Rolle im Konfliktmanagement. Sie benötigen zur erfolgreichen Konfliktlösung Kommunikationsfähigkeiten, Empathie, Neutralität und Durchsetzungsfähigkeit. Diese Kompetenzen können durch Seminare und Coachings gezielt verbessert werden. Führungskräfte sollten regelmäßig geschult werden, um Konflikte frühzeitig zu erkennen und professionell darauf zu reagieren.